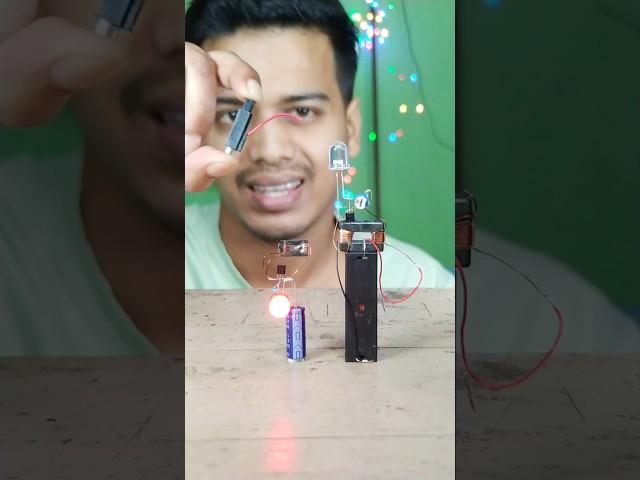
Static - Triggered Circuit #diyprojects #diycircuit #diy #led #electric #electronic #experiment
An electroscope is a device used to detect and measure the presence of electric charges. It's a simple, yet fascinating tool that has been used for centuries to explore the properties of electricity.
How an Electroscope Works:
A typical electroscope consists of a metal rod or sphere attached to a metal leaf or a thin metal strip. The metal rod or sphere is usually insulated from the surrounding environment.
Here's what happens when an electroscope is brought near a charged object:
1. If the object is positively charged, it will attract electrons from the electroscope's metal rod or sphere.
2. The metal leaf or strip will then be attracted to the metal rod or sphere, causing it to move or diverge.
3. If the object is negatively charged, it will repel electrons from the electroscope's metal rod or sphere.
4. The metal leaf or strip will then be repelled by the metal rod or sphere, causing it to move or diverge in the opposite direction.
Types of Electroscopes:
There are several types of electroscopes, including:
1. Gold Leaf Electroscope: This is the most common type of electroscope, which uses a gold leaf to detect electric charges.
2. Pith Ball Electroscope: This type of electroscope uses a small pith ball (a lightweight, hollow sphere) to detect electric charges.
3. Metal Leaf Electroscope: This type of electroscope uses a thin metal leaf to detect electric charges.
Applications of Electroscopes:
Electroscopes have been used in various applications, including:
1. Detecting Electric Charges: Electroscopes are used to detect the presence of electric charges on objects.
2. Measuring Electric Fields: Electroscopes can be used to measure the strength of electric fields.
3. Demonstrating Electrostatic Principles: Electroscopes are often used in educational settings to demonstrate electrostatic principles, such as the attraction and repulsion of electric charges.
A digital electroscope is an electronic device that measures and displays the presence and magnitude of electric charges or electric fields. It's a modern version of the traditional electroscope, but with digital capabilities.
Key Features of a Digital Electroscope:
1. Digital Display: Shows the measured electric charge or electric field strength in numerical format.
2. High Sensitivity: Can detect very small electric charges or electric fields.
3. Wide Range: Can measure electric charges or electric fields over a wide range of values.
4. Accuracy: Provides accurate measurements, often with a high degree of precision.
5. Ease of Use: Often features a simple, user-friendly interface.
Types of Digital Electroscopes:
1. Field Mill Electroscope: Uses a rotating field mill to measure the electric field strength.
2. Electrometer Electroscope: Uses an electrometer to measure the electric charge or electric field strength.
3. Digital Electrometer Electroscope: Combines the functions of an electrometer and a digital display.
Applications of Digital Electroscopes:
1. Electrostatic Research: Used in research applications to study electrostatic phenomena.
2. Electrical Engineering: Used in electrical engineering applications to measure and analyze electric fields.
3. Quality Control: Used in manufacturing and quality control applications to detect and measure electrostatic charges.
4. Education: Used in educational settings to teach students about electrostatic principles.
Digital electroscopes offer several advantages over traditional electroscopes, including higher sensitivity, wider range, and greater accuracy.
How an Electroscope Works:
A typical electroscope consists of a metal rod or sphere attached to a metal leaf or a thin metal strip. The metal rod or sphere is usually insulated from the surrounding environment.
Here's what happens when an electroscope is brought near a charged object:
1. If the object is positively charged, it will attract electrons from the electroscope's metal rod or sphere.
2. The metal leaf or strip will then be attracted to the metal rod or sphere, causing it to move or diverge.
3. If the object is negatively charged, it will repel electrons from the electroscope's metal rod or sphere.
4. The metal leaf or strip will then be repelled by the metal rod or sphere, causing it to move or diverge in the opposite direction.
Types of Electroscopes:
There are several types of electroscopes, including:
1. Gold Leaf Electroscope: This is the most common type of electroscope, which uses a gold leaf to detect electric charges.
2. Pith Ball Electroscope: This type of electroscope uses a small pith ball (a lightweight, hollow sphere) to detect electric charges.
3. Metal Leaf Electroscope: This type of electroscope uses a thin metal leaf to detect electric charges.
Applications of Electroscopes:
Electroscopes have been used in various applications, including:
1. Detecting Electric Charges: Electroscopes are used to detect the presence of electric charges on objects.
2. Measuring Electric Fields: Electroscopes can be used to measure the strength of electric fields.
3. Demonstrating Electrostatic Principles: Electroscopes are often used in educational settings to demonstrate electrostatic principles, such as the attraction and repulsion of electric charges.
A digital electroscope is an electronic device that measures and displays the presence and magnitude of electric charges or electric fields. It's a modern version of the traditional electroscope, but with digital capabilities.
Key Features of a Digital Electroscope:
1. Digital Display: Shows the measured electric charge or electric field strength in numerical format.
2. High Sensitivity: Can detect very small electric charges or electric fields.
3. Wide Range: Can measure electric charges or electric fields over a wide range of values.
4. Accuracy: Provides accurate measurements, often with a high degree of precision.
5. Ease of Use: Often features a simple, user-friendly interface.
Types of Digital Electroscopes:
1. Field Mill Electroscope: Uses a rotating field mill to measure the electric field strength.
2. Electrometer Electroscope: Uses an electrometer to measure the electric charge or electric field strength.
3. Digital Electrometer Electroscope: Combines the functions of an electrometer and a digital display.
Applications of Digital Electroscopes:
1. Electrostatic Research: Used in research applications to study electrostatic phenomena.
2. Electrical Engineering: Used in electrical engineering applications to measure and analyze electric fields.
3. Quality Control: Used in manufacturing and quality control applications to detect and measure electrostatic charges.
4. Education: Used in educational settings to teach students about electrostatic principles.
Digital electroscopes offer several advantages over traditional electroscopes, including higher sensitivity, wider range, and greater accuracy.
Тэги:
#diy #electroscope #static_charge_device #static_charge #diy_projects #diy_electric #electronic #electric #led #battery #school_science_project #science_project #college_project #voltage_generator #voltage_booster #booster_circuit #boost_converter #electronic_engineering #engineeringКомментарии:
Ирина Жукова + шоу балет Романтик Ведьмина вода
Irina Kober
Philippine martial art "Panantukan"
Путь Воина




![ANIMAL X RANVIJAY... • RANBIR KAPOOR ATTITUDE.. [4K] QUALITY HDR EDIT... #animal #ranbirkapoor ANIMAL X RANVIJAY... • RANBIR KAPOOR ATTITUDE.. [4K] QUALITY HDR EDIT... #animal #ranbirkapoor](https://smotrel.cc/img/upload/VVJ1dGZ1NEtOUXI.jpg)